Introduction to Database
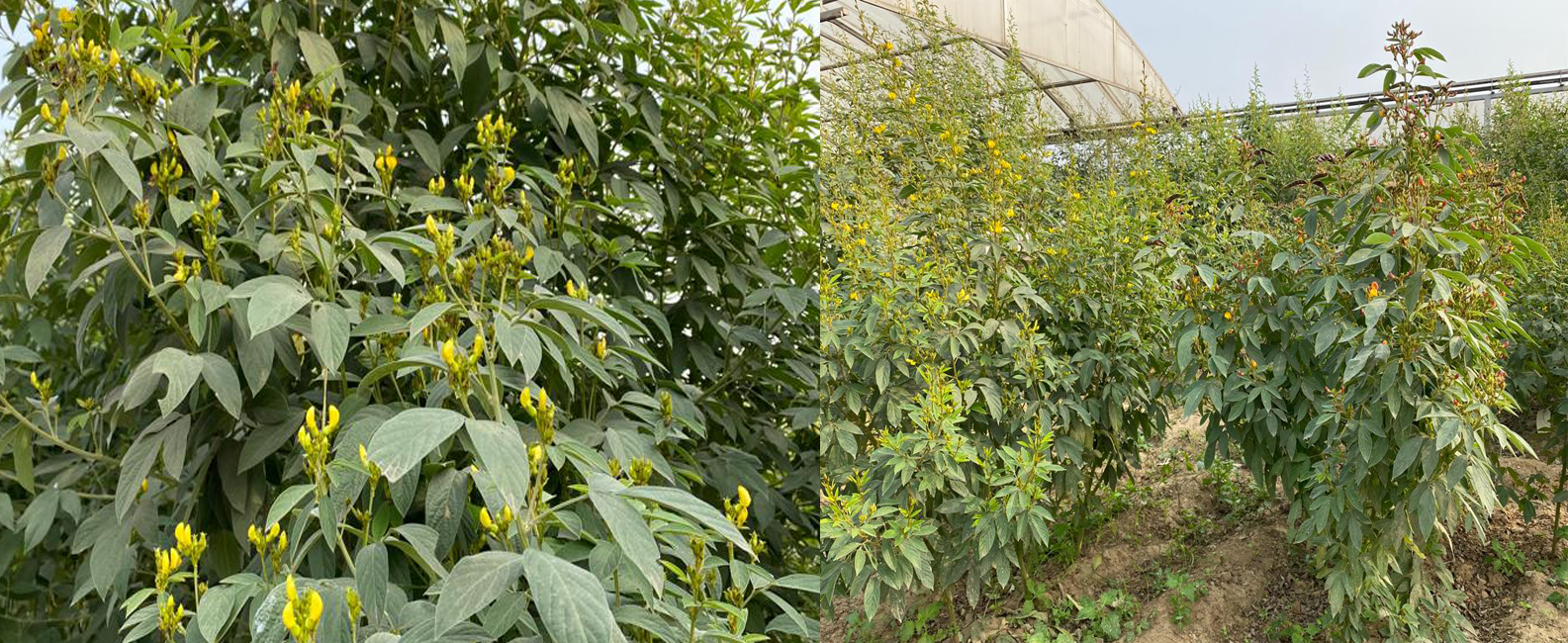
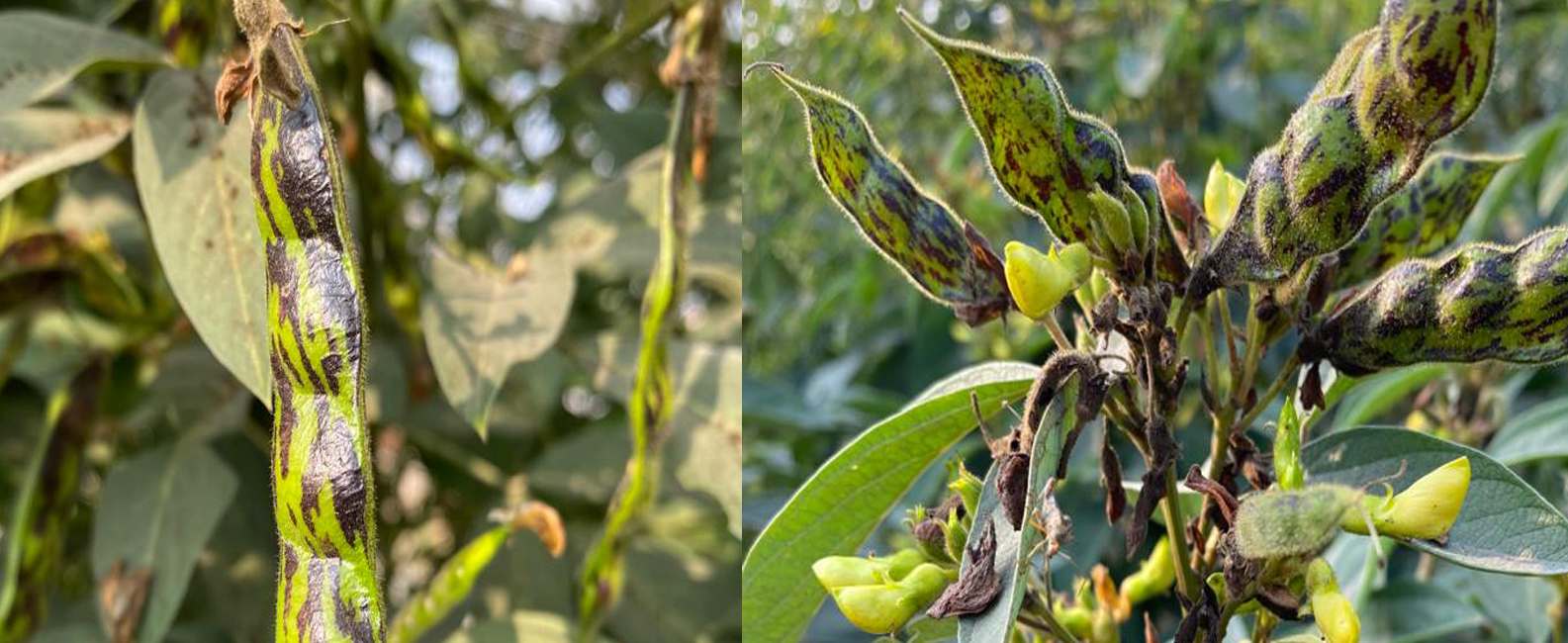
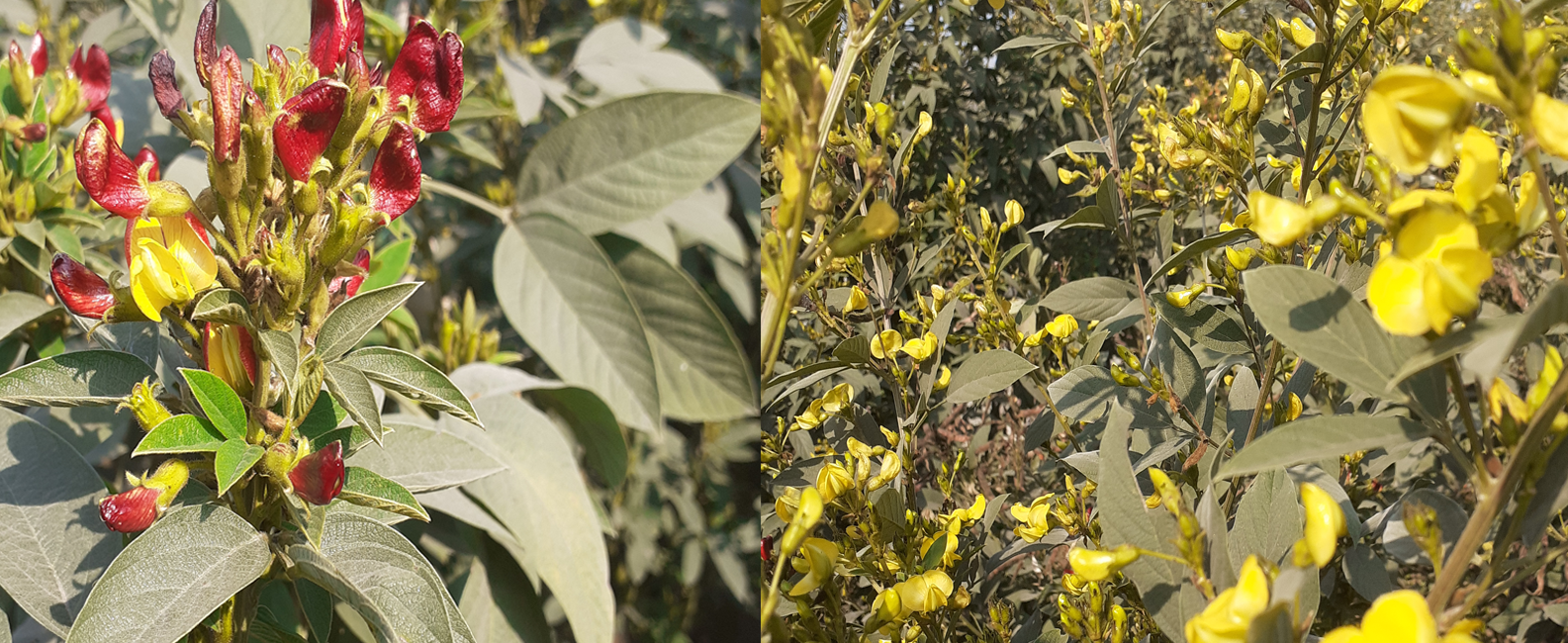
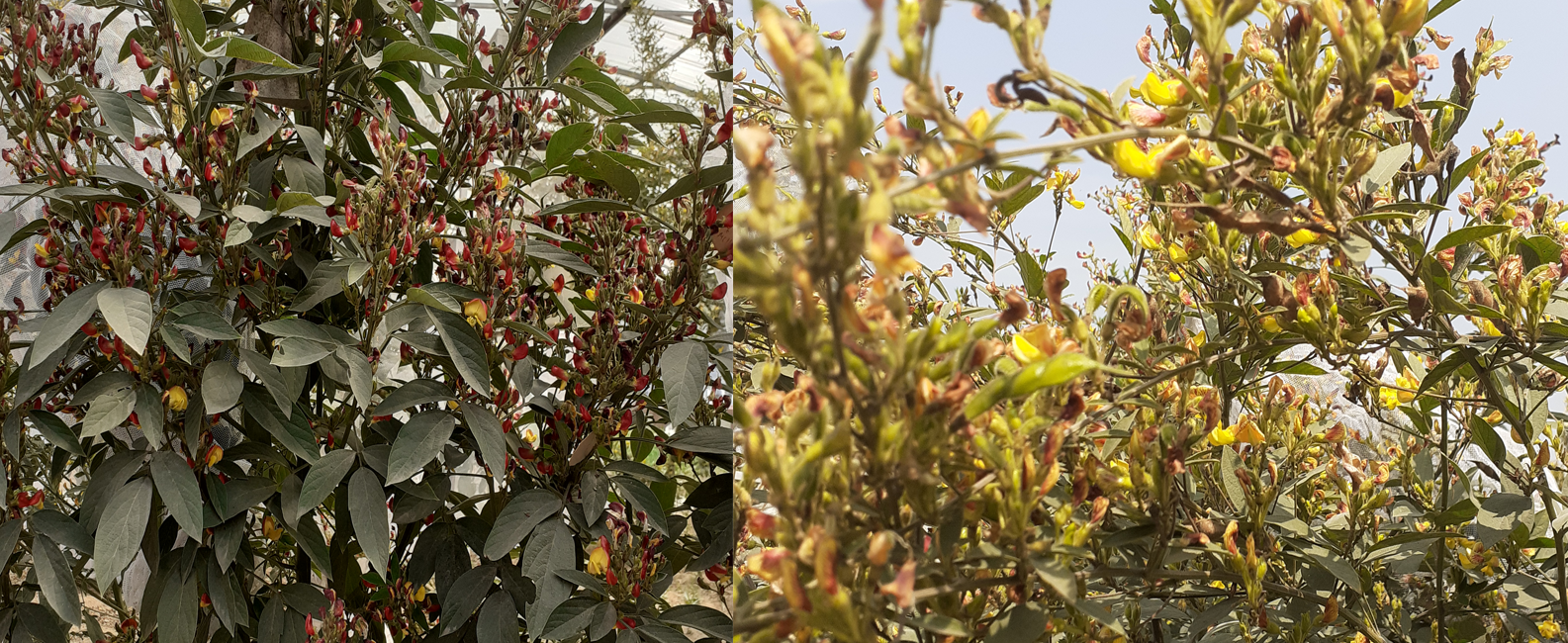
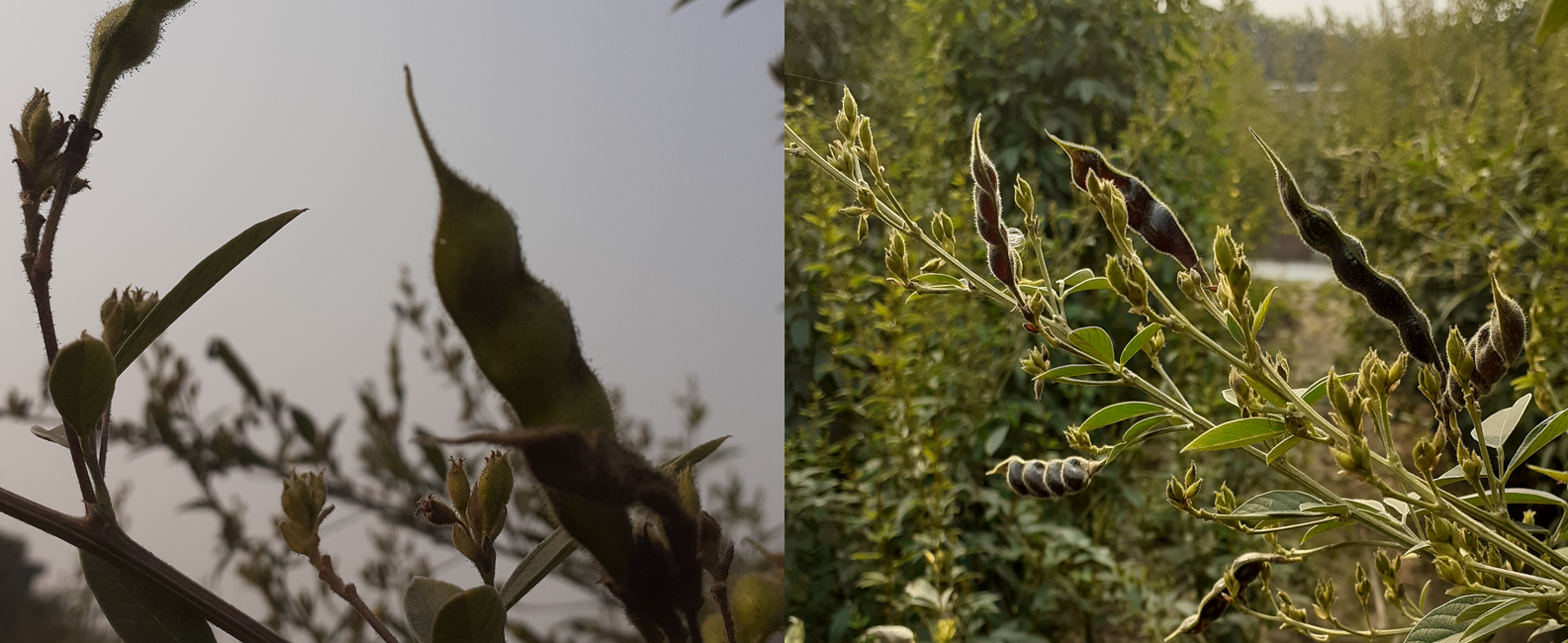
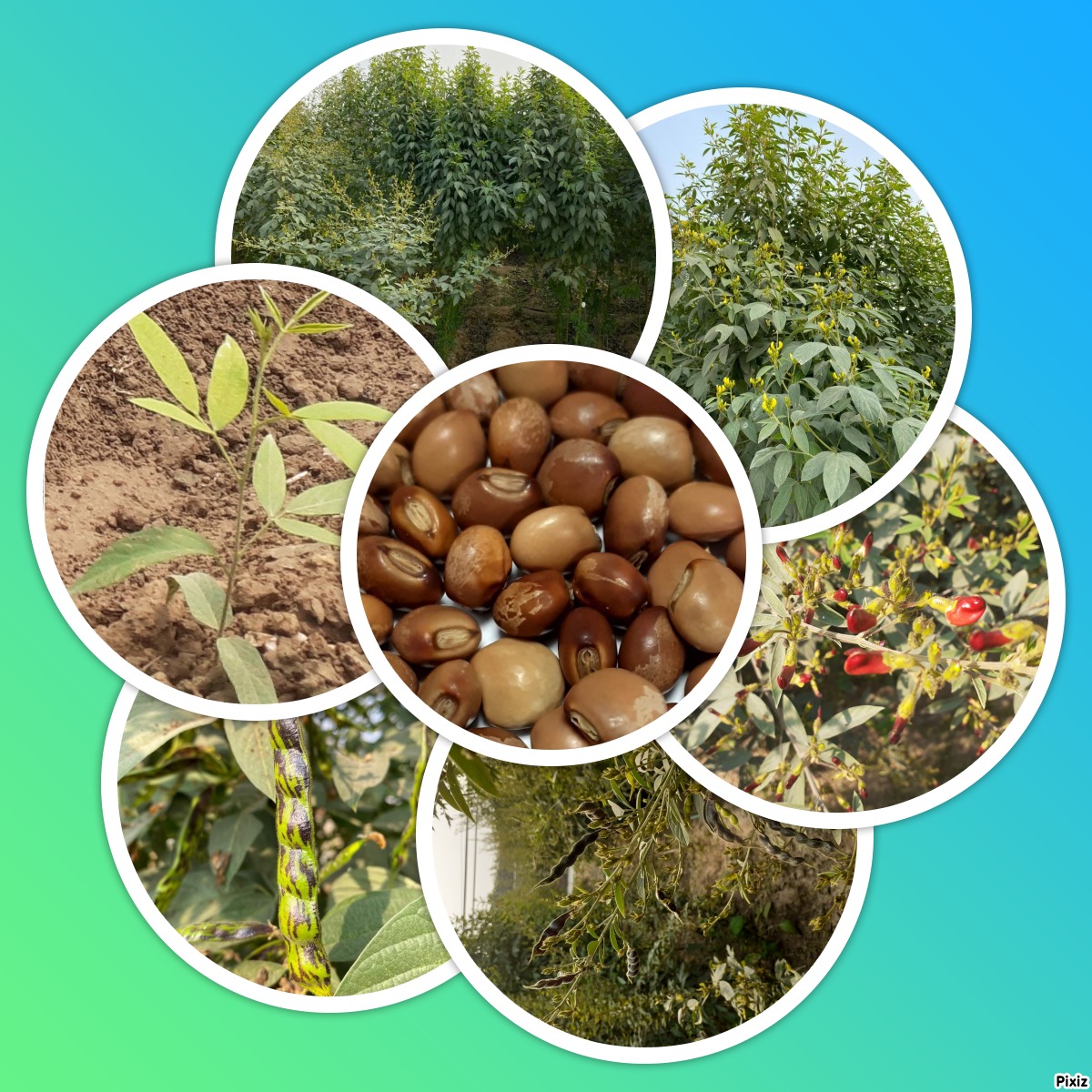
The pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.) is a significant grain legume crop of the tropics and subtropics. It has numerous uses as food, feed, fuel, a soil enricher or soil binder, as well as in fencing, roofing, and basket manufacturing. It is a diploid (2n=2x-22) with an estimated genome size of 858 Mb. The closest wild relative of pigeonpea is Cajanus cajanifolius. It is a great source of protein, minerals, and vitamins. Its seeds are composed of 85% cotyledons, 14% seed coat, about 1% embryo, and contain a variety of dietary nutrients. Huge diversity exists in the seed of pigeonpea, including seed coat color, size, texture, and taste.


Dr. Nisha Singh, PhD
Assistant Professor – Bioinformatics (DST INSPIRE FACULTY – PI)

Prof. Nagandra Kumar Singh, PhD
ICAR-National professor(B P Pal Chair), JC Bose National Fellow

Megha Ujinwal
PhD Student
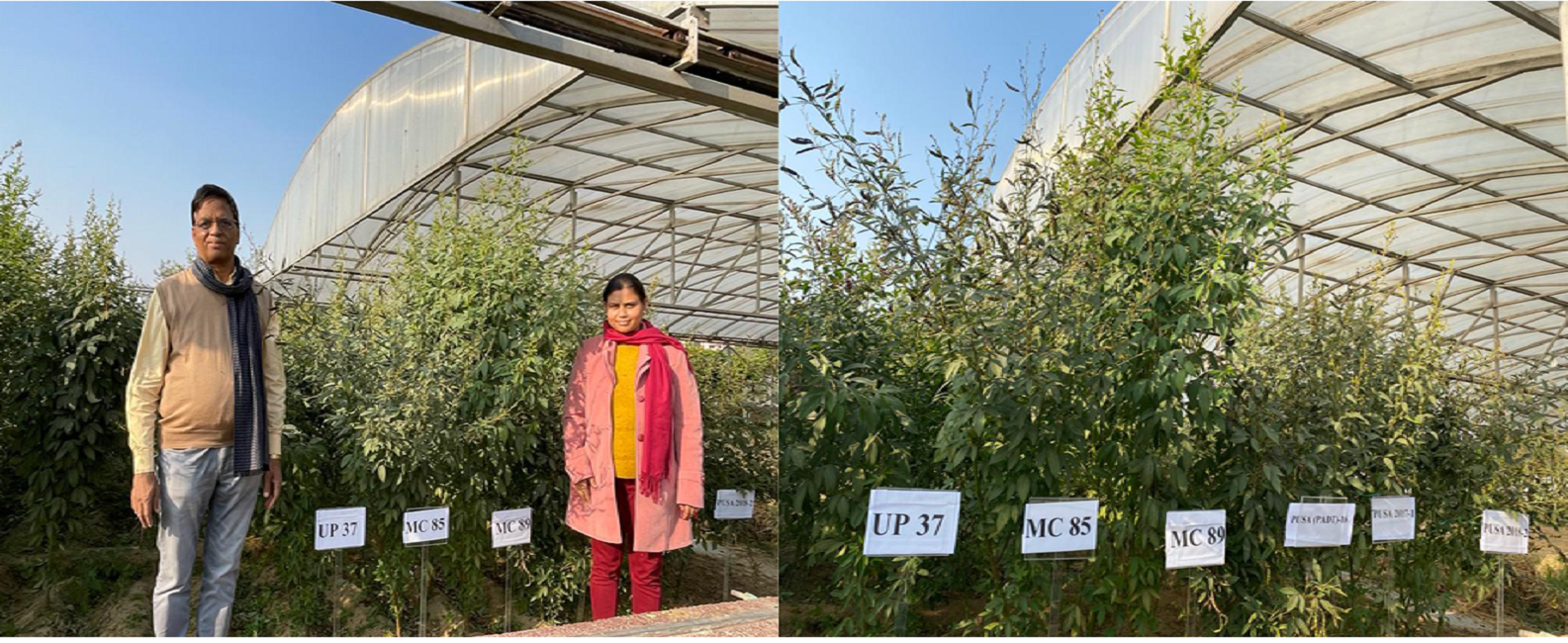
Pigeonpea Germplasm

MC 94

UP 111-I

UP 92-VIII

UP 8-I

MC 93

MC 26

ICPL-14923

DG(RG)-15

ICPL-13852

ICPL-13438

MC 94

UP 111-I

UP 92-VIII

UP 8-I

MC 93

MC 26

ICPL-14923

DG(RG)-15

ICPL-13852

ICPL-13438